Show the code
library(tidyverse)
library(BayesERtools)
library(posterior)
library(tidybayes)
library(bayesplot)
library(loo)
library(here)
library(gt)
theme_set(theme_bw(base_size = 12))This page showcase the model diagnosis and comparison for the Emax model
library(tidyverse)
library(BayesERtools)
library(posterior)
library(tidybayes)
library(bayesplot)
library(loo)
library(here)
library(gt)
theme_set(theme_bw(base_size = 12))d_sim_emax# A tibble: 300 × 9
dose exposure response_1 response_2 cnt_a cnt_b cnt_c bin_d bin_e
set.seed(1234)
ermod_sigemax <- dev_ermod_emax(
data = d_sim_emax,
var_resp = "response_1",
var_exposure = "exposure",
gamma_fix = NULL
)
ermod_sigemax
── Emax model ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
ℹ Use `plot_er()` to visualize ER curve
── Developed model ──
---- Emax model fit with rstanemax ----
mean se_mean sd 2.5% 25% 50% 75% 97.5% n_eff
emax 11.59 0.31 5.89 4.82 7.34 10.10 14.24 27.50 368.24
e0 6.68 0.20 4.08 -3.67 4.78 7.68 9.71 11.48 436.14
ec50 5254.72 193.00 4475.71 801.17 2974.18 4673.97 6385.68 15736.00 537.81
gamma 1.06 0.02 0.50 0.32 0.70 0.97 1.33 2.26 543.20
sigma 1.27 0.00 0.05 1.18 1.24 1.27 1.31 1.39 1375.87
Rhat
emax 1.01
e0 1.01
ec50 1.00
gamma 1.01
sigma 1.00
* Use `extract_stanfit()` function to extract raw stanfit object
* Use `extract_param()` function to extract posterior draws of key parameters
* Use `plot()` function to visualize model fit
* Use `posterior_predict()` or `posterior_predict_quantile()` function to get
raw predictions or make predictions on new data
* Use `extract_obs_mod_frame()` function to extract raw data
in a processed format (useful for plotting)
Another model without sigmoidal component; will be used when we do model comparison.
set.seed(1234)
ermod_emax <- dev_ermod_emax(
data = d_sim_emax,
var_resp = "response_1",
var_exposure = "exposure",
gamma_fix = 1
)
ermod_emax
── Emax model ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
ℹ Use `plot_er()` to visualize ER curve
── Developed model ──
---- Emax model fit with rstanemax ----
mean se_mean sd 2.5% 25% 50% 75% 97.5% n_eff
emax 10.11 0.07 1.71 7.93 8.98 9.72 10.81 14.42 564.00
e0 7.32 0.08 2.00 2.41 6.41 7.66 8.70 10.13 572.38
ec50 4341.84 62.80 1871.39 1704.41 3062.61 3994.85 5323.78 9061.88 887.87
gamma 1.00 NaN 0.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 NaN
sigma 1.28 0.00 0.05 1.18 1.24 1.27 1.31 1.39 1440.04
Rhat
emax 1.01
e0 1.01
ec50 1.00
gamma NaN
sigma 1.00
* Use `extract_stanfit()` function to extract raw stanfit object
* Use `extract_param()` function to extract posterior draws of key parameters
* Use `plot()` function to visualize model fit
* Use `posterior_predict()` or `posterior_predict_quantile()` function to get
raw predictions or make predictions on new data
* Use `extract_obs_mod_frame()` function to extract raw data
in a processed format (useful for plotting)
d_draws_sigemax_summary <-
summarize_draws(ermod_sigemax)
d_draws_sigemax_summary |>
gt() |>
fmt_number(decimals = 2)
```{=html}
variable
mean
median
sd
mad
q5
q95
rhat
ess_bulk
ess_tail
ec50
5,254.72
4,673.97
4,475.71
2,534.11
1,125.57
9,837.30
1.01
614.40
541.30
sigma
1.27
1.27
0.05
0.05
1.19
1.36
1.00
1,379.24
1,505.63
gamma
1.06
0.97
0.50
0.45
0.40
2.04
1.01
459.99
555.58
e0
6.68
7.68
4.08
3.42
−1.45
11.20
1.01
480.68
788.66
emax
11.59
10.10
5.89
4.79
5.20
23.06
1.01
429.41
533.51
```
Here is the example of highest-density continuous interval (HDCI) for the median of ED50. See here for more details.
# HDCI of median.ED50
as_draws_df(ermod_sigemax) |>
tidybayes::spread_rvars(ec50) |>
tidybayes::median_hdci()# A tibble: 1 × 6
ec50 .lower .upper .width .point .interval
Fitted values without residual errors (i.e. PRED in NONMEM term) can be extracted with sim_er() function. .epred is the expected value prediction. See ?sim_er for detail.
sim_er(ermod_sigemax) |> head()# A tibble: 6 × 16
# Groups: dose, exposure, response_1, response_2, cnt_a, cnt_b, cnt_c, bin_d,
# bin_e, .row [1]
dose exposure response_1 response_2 cnt_a cnt_b cnt_c bin_d bin_e .row
, .iteration , .draw ,
# .epred , .linpred , .prediction
You can specify output_type = "median_qi" to get median and quantile intervals of the prediction.
ersim_sigemax_med_qi <-
sim_er(ermod_sigemax, output_type = "median_qi")
ersim_sigemax_med_qi |>
arrange(.row) |>
head() |>
gt(rownames_to_stub = TRUE) |>
fmt_number(decimals = 2, columns = -.row)
```{=html}
dose
exposure
response_1
response_2
cnt_a
cnt_b
cnt_c
bin_d
bin_e
.row
.epred
.epred.lower
.epred.upper
.linpred
.linpred.lower
.linpred.upper
.prediction
.prediction.lower
.prediction.upper
.width
.point
.interval
1
100.00
4,151.15
12.80
1.00
5.71
2.33
7.83
0.00
1.00
1
12.62
12.33
12.92
12.62
12.33
12.92
12.63
10.03
15.29
0.95
median
qi
2
100.00
8,067.26
14.58
1.00
4.92
4.66
6.74
1.00
1.00
2
14.14
13.93
14.35
14.14
13.93
14.35
14.14
11.69
16.69
0.95
median
qi
3
100.00
4,877.67
12.76
1.00
4.88
4.21
4.68
1.00
1.00
3
13.00
12.73
13.24
13.00
12.73
13.24
12.98
10.52
15.51
0.95
median
qi
4
100.00
9,712.93
16.55
1.00
8.42
6.56
1.29
0.00
1.00
4
14.53
14.31
14.74
14.53
14.31
14.74
14.51
12.07
17.07
0.95
median
qi
5
100.00
11,490.74
14.41
0.00
4.37
3.96
3.55
0.00
1.00
5
14.86
14.64
15.08
14.86
14.64
15.08
14.87
12.36
17.37
0.95
median
qi
6
100.00
2,451.55
12.60
1.00
8.69
7.60
3.64
0.00
0.00
6
11.48
10.87
12.07
11.48
10.87
12.07
11.47
8.86
14.00
0.95
median
qi
```
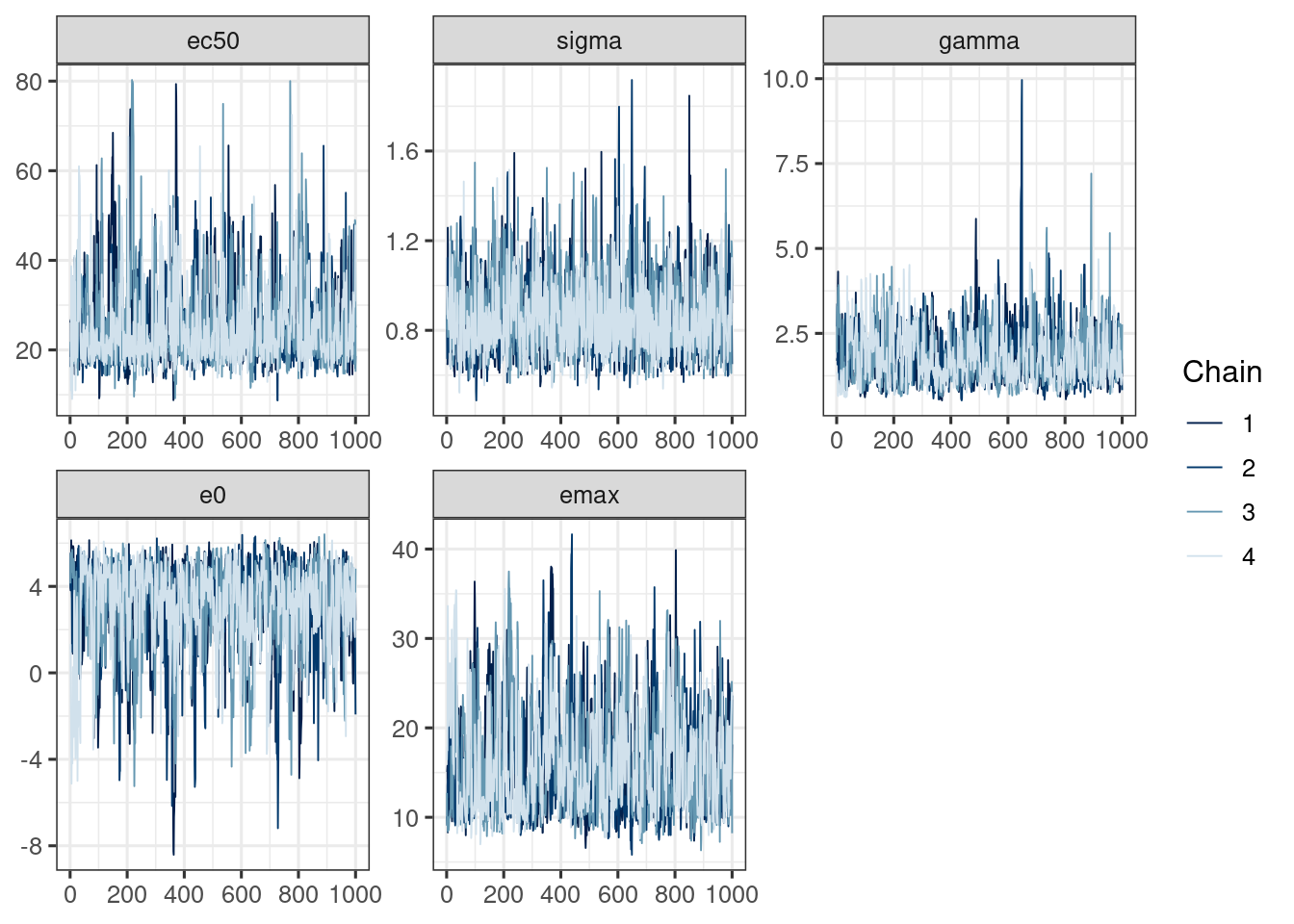
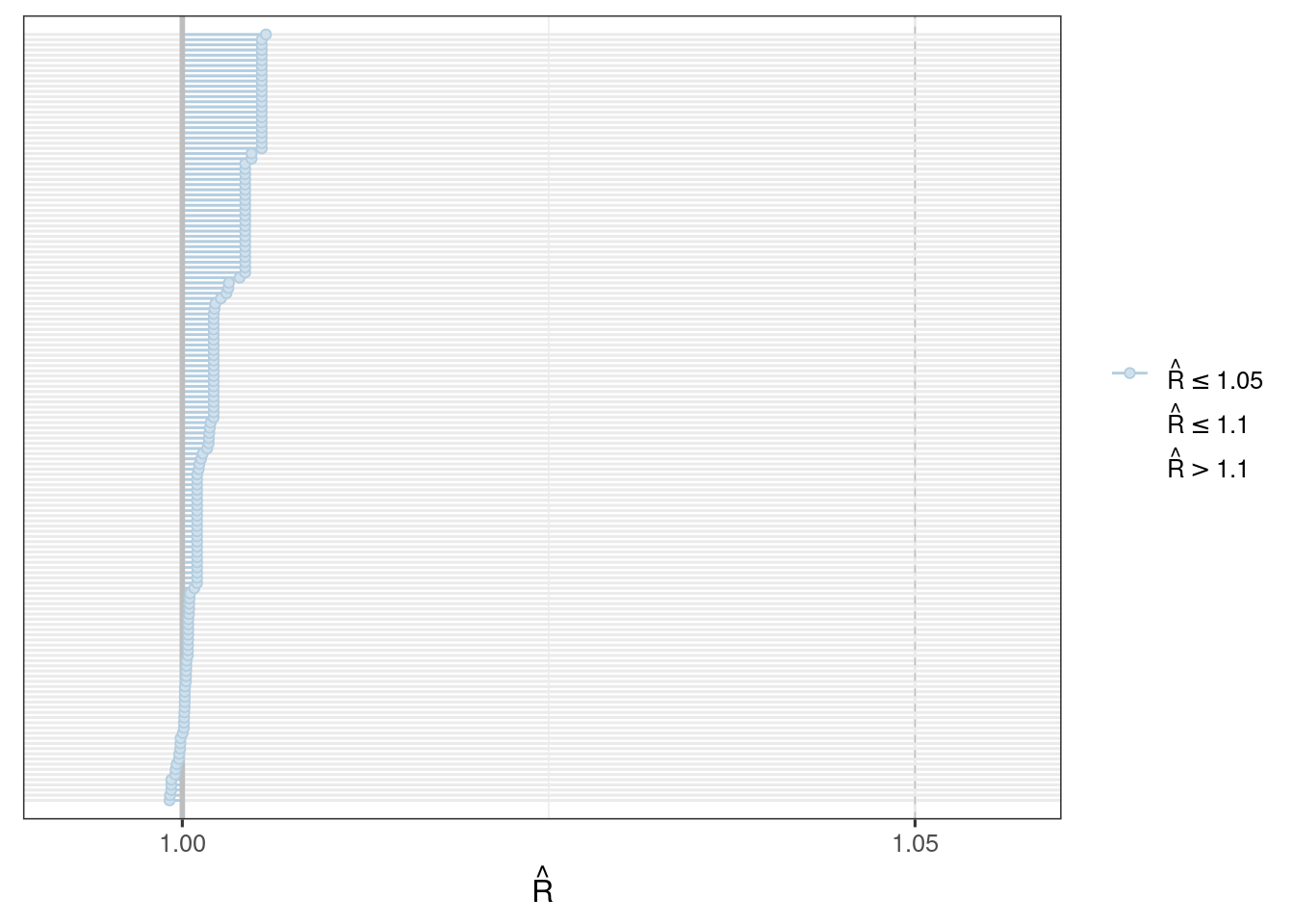
We use the bayesplot package (Cheat sheet) to visualize the model fit.
Good fit results in:
Rhat close to 1 (e.g. < 1.1)d_draws_sigemax <- as_draws_df(ermod_sigemax)
mcmc_dens_overlay(d_draws_sigemax)Warning: Using `size` aesthetic for lines was deprecated in ggplot2 3.4.0.
ℹ Please use `linewidth` instead.
ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the bayesplot package.
Please report the issue at mcmc_trace(d_draws_sigemax)
mcmc_rhat(rhat(ermod_sigemax$mod$stanfit))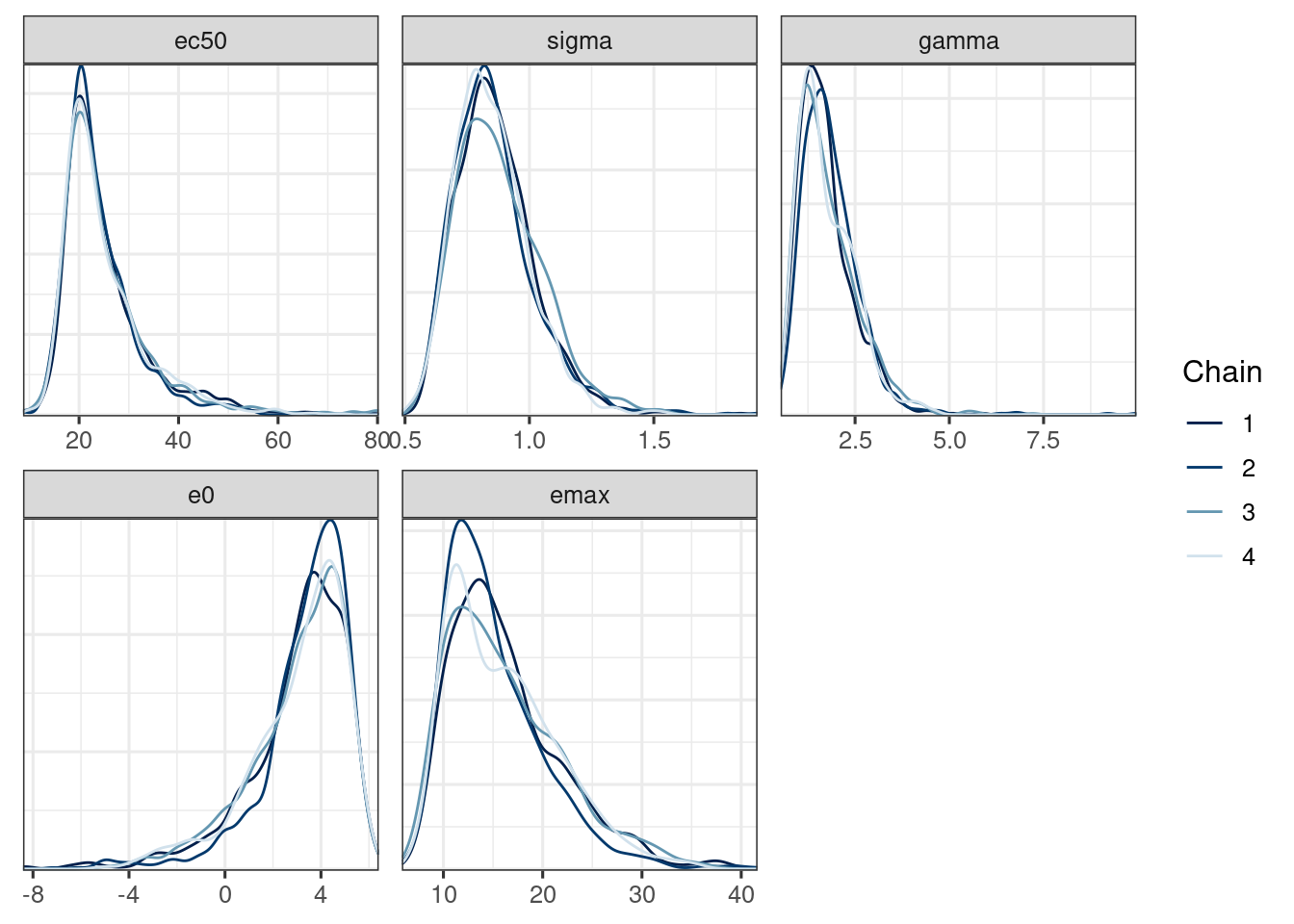
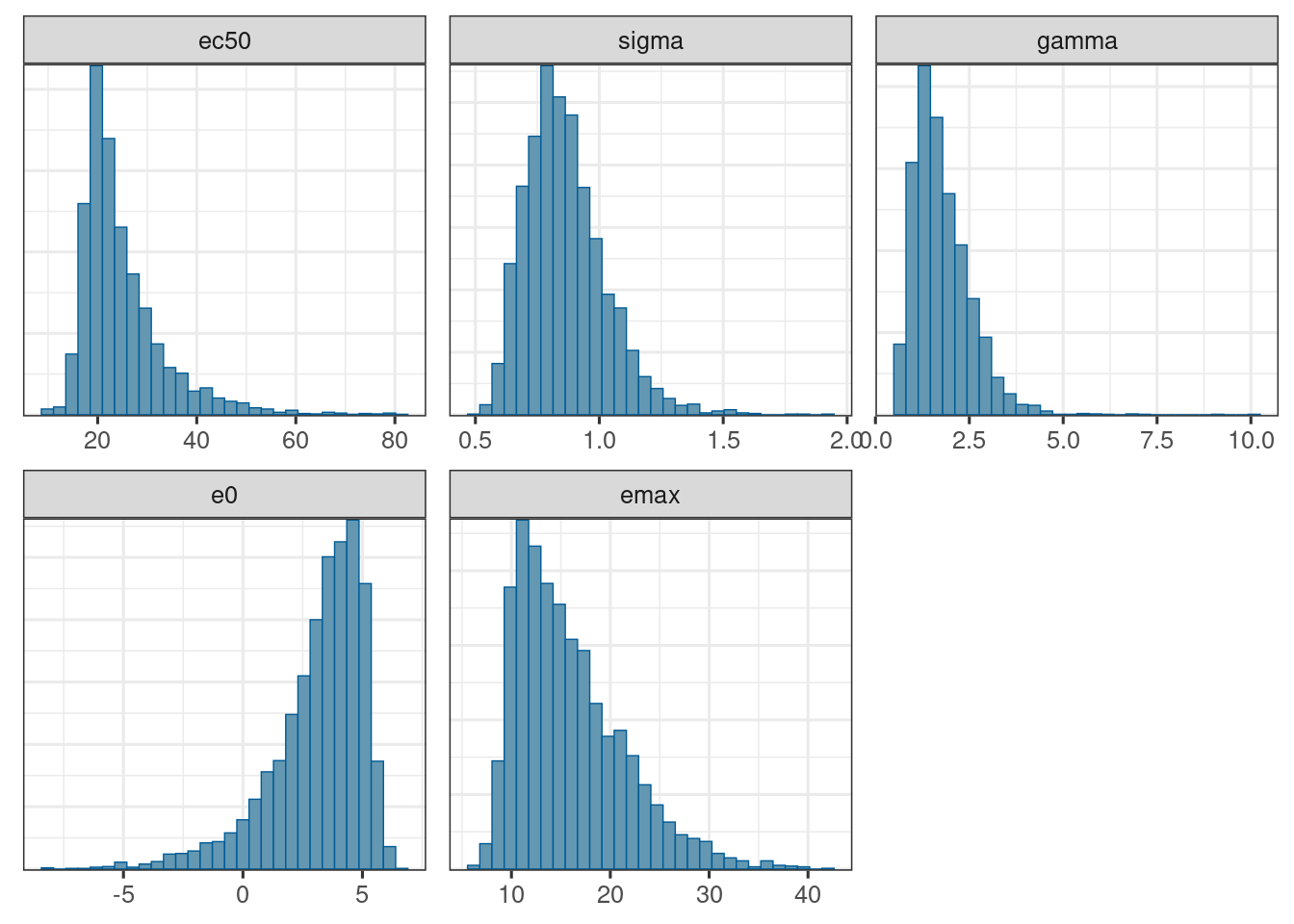
mcmc_hist(d_draws_sigemax)`stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value `binwidth`.
mcmc_pairs(d_draws_sigemax,
off_diag_args = list(size = 0.5, alpha = 0.25))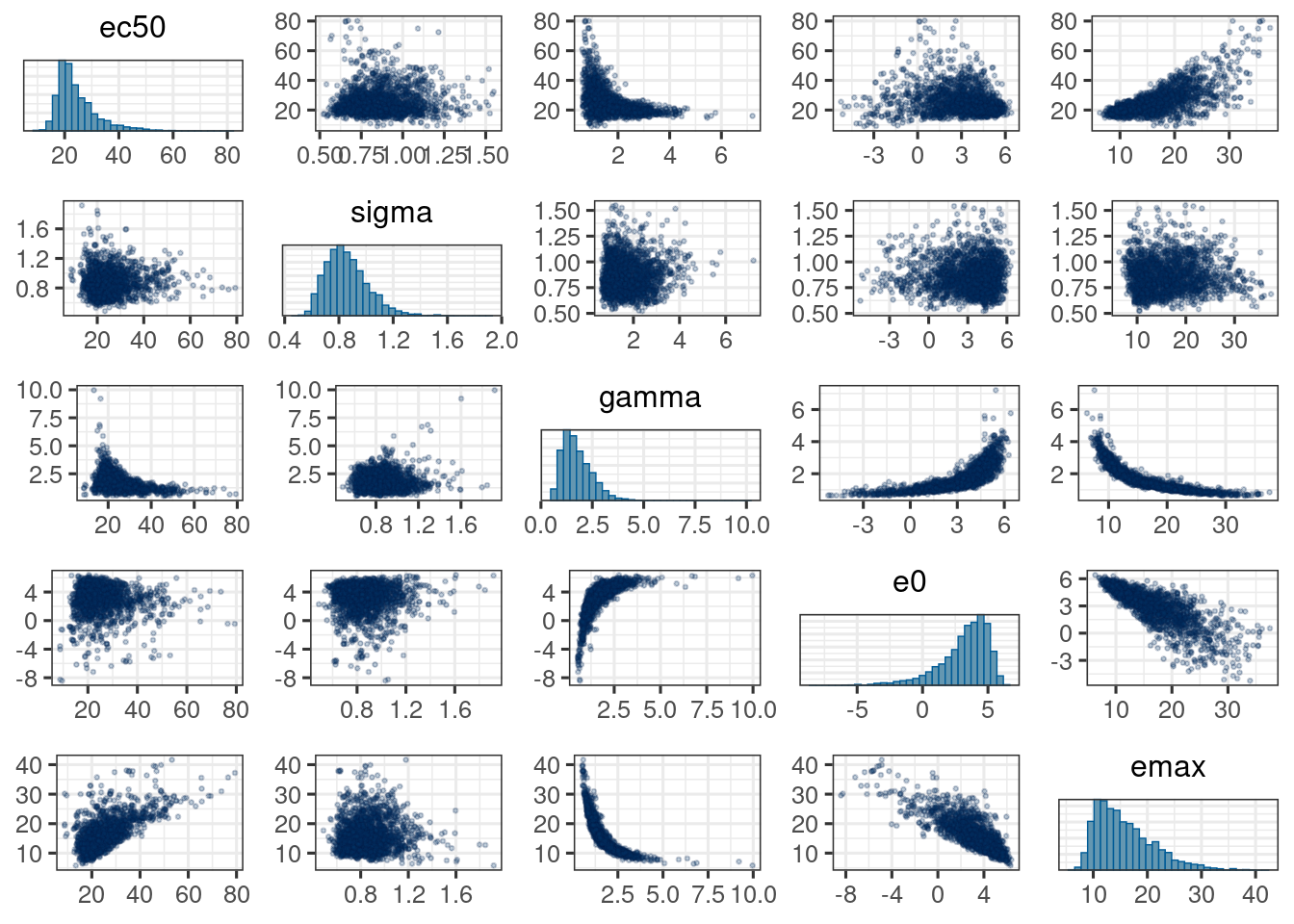
plot_er(ermod_sigemax, show_orig_data = TRUE)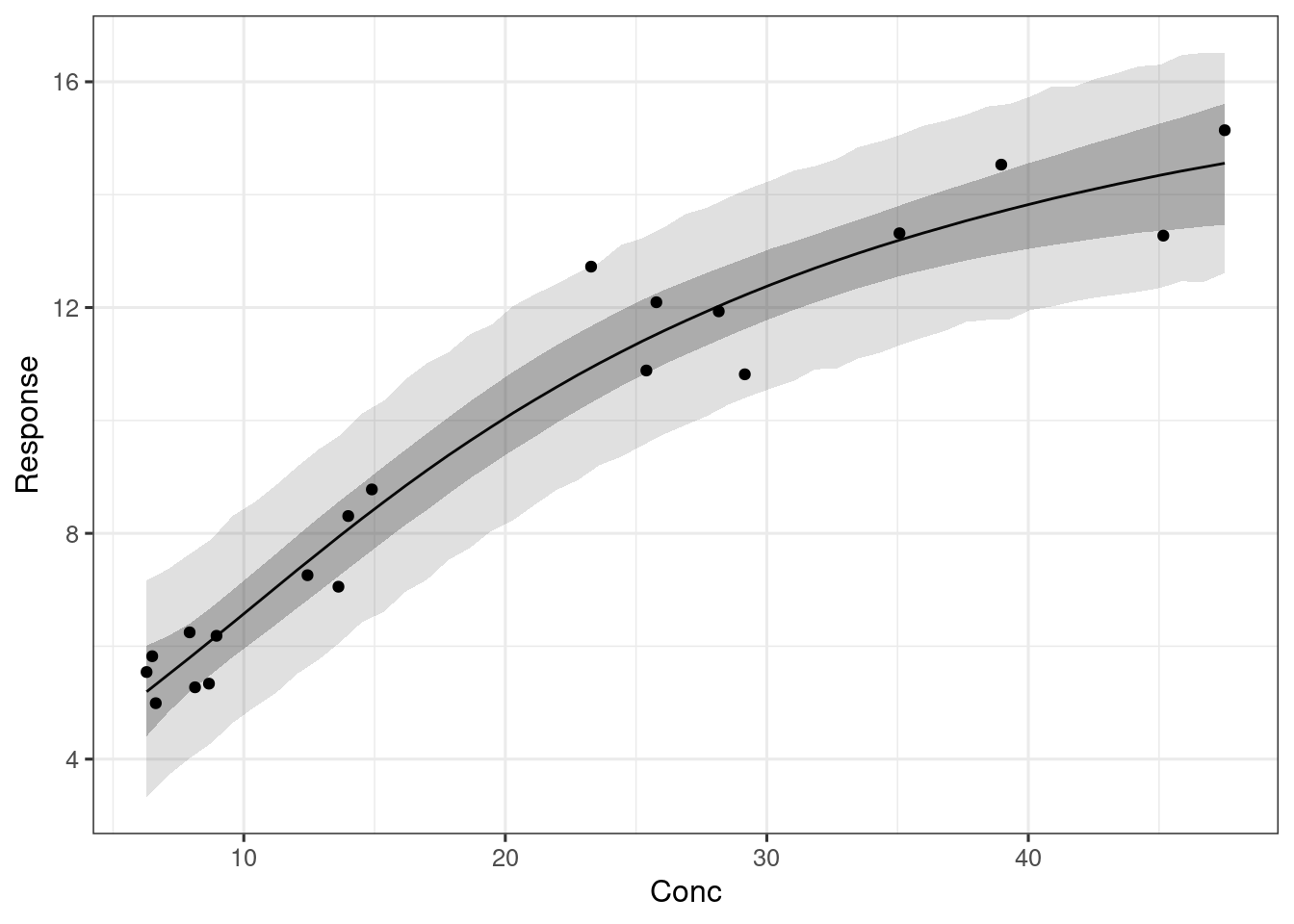
# Preparation for diagnostic plots
ersim_sigemax_med_qi <- sim_er(ermod_sigemax, output_type = "median_qi")
ersim_sigemax_med_qi |>
ggplot(aes(x = .epred, y = response_1)) +
geom_smooth(method = "loess", formula = y ~ x) +
geom_abline(linetype = 2, color = "grey") +
geom_point() +
geom_errorbar(
mapping = aes(xmin = .epred.lower, xmax = .epred.upper),
orientation = "y"
) +
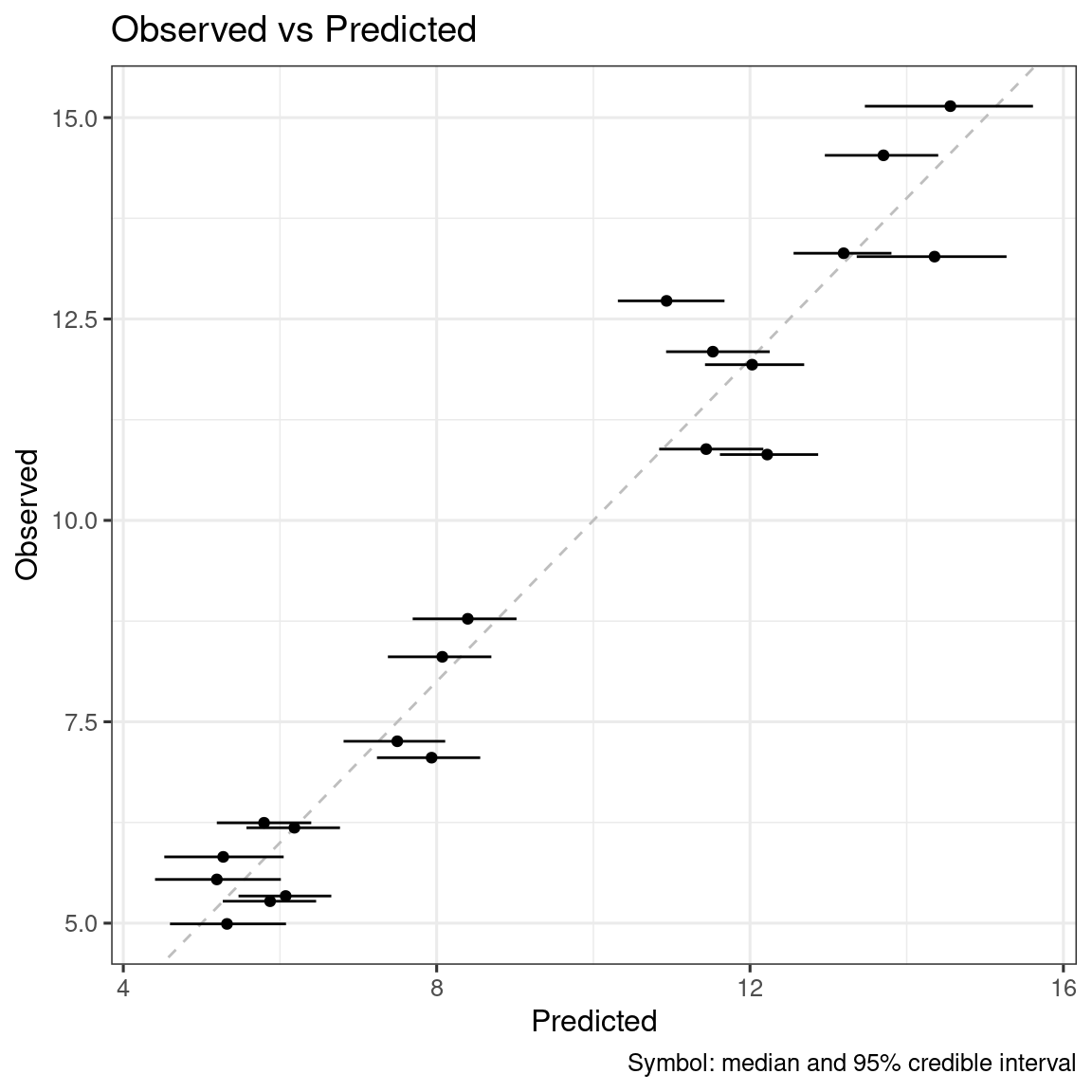
labs(
title = "Observed vs Predicted",
x = "Predicted",
y = "Observed",
caption = "Symbol: median and 95% credible interval"
)
ersim_sigemax_w_resid <-
sim_er(ermod_sigemax) |>
mutate(.residual = response_1 - .epred) # Add residuals for plotting
ersim_sigemax_w_resid_med_qi <- median_qi(ersim_sigemax_w_resid)
ersim_sigemax_w_resid_med_qi |>
ggplot(aes(x = .epred, y = .residual)) +
xlab("Predicted (linear)") +
ylab("Residuals") +
geom_smooth(method = "loess", formula = y ~ x) +
geom_point() +
geom_errorbar(
mapping = aes(ymin = .residual.lower, ymax = .residual.upper),
width = 0
) +
geom_hline(aes(yintercept = 2), lty = 2, colour = "grey70") +
geom_hline(aes(yintercept = -2), lty = 2, colour = "grey70")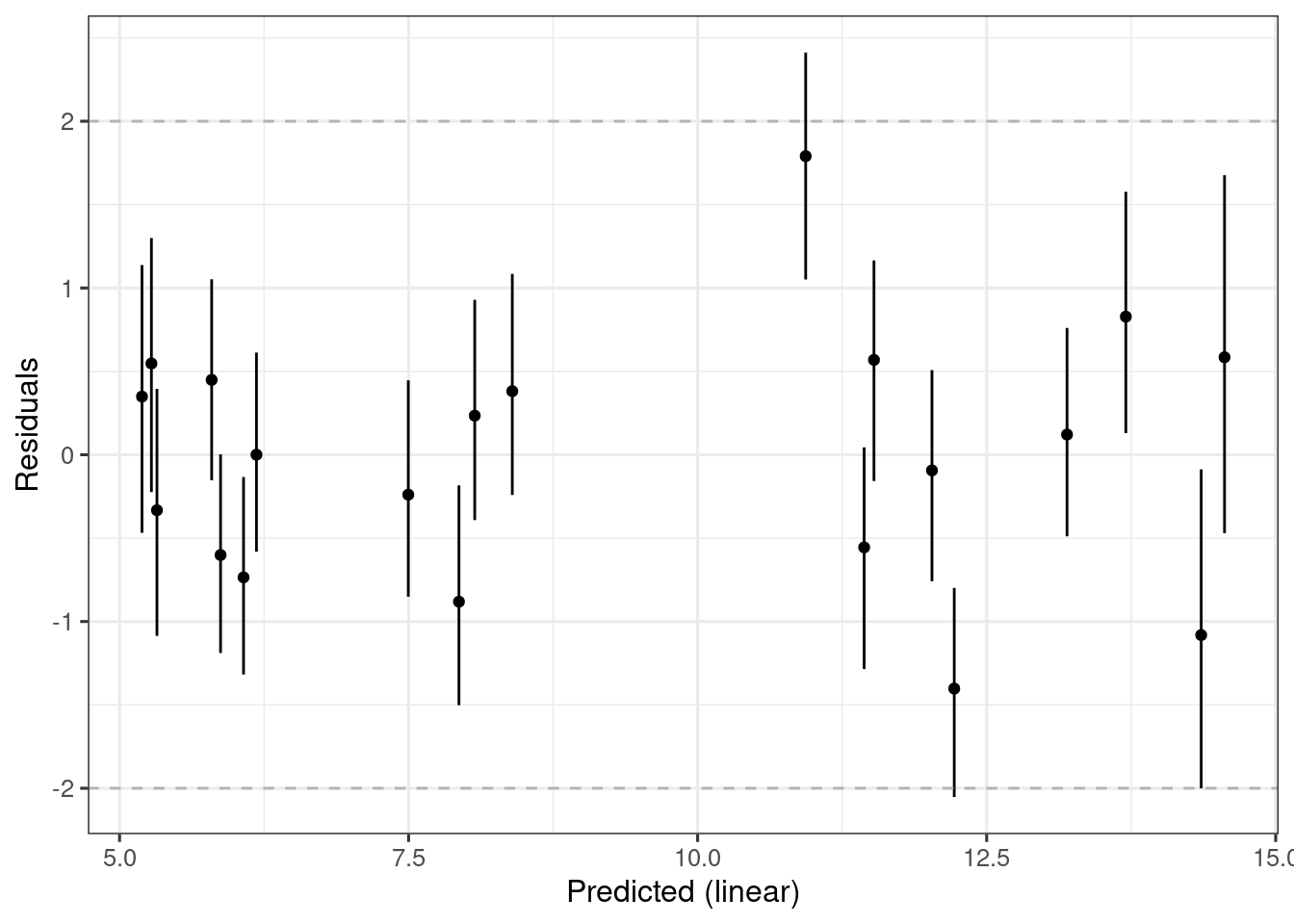
ersim_sigemax_w_resid_med_qi |>
ggplot(aes(sample = .residual)) +
geom_qq() +
geom_qq_line(colour = "steelblue", lty = 2, alpha = 0.4) +
coord_equal() +
labs(x = "Theoretical", y = "Sample")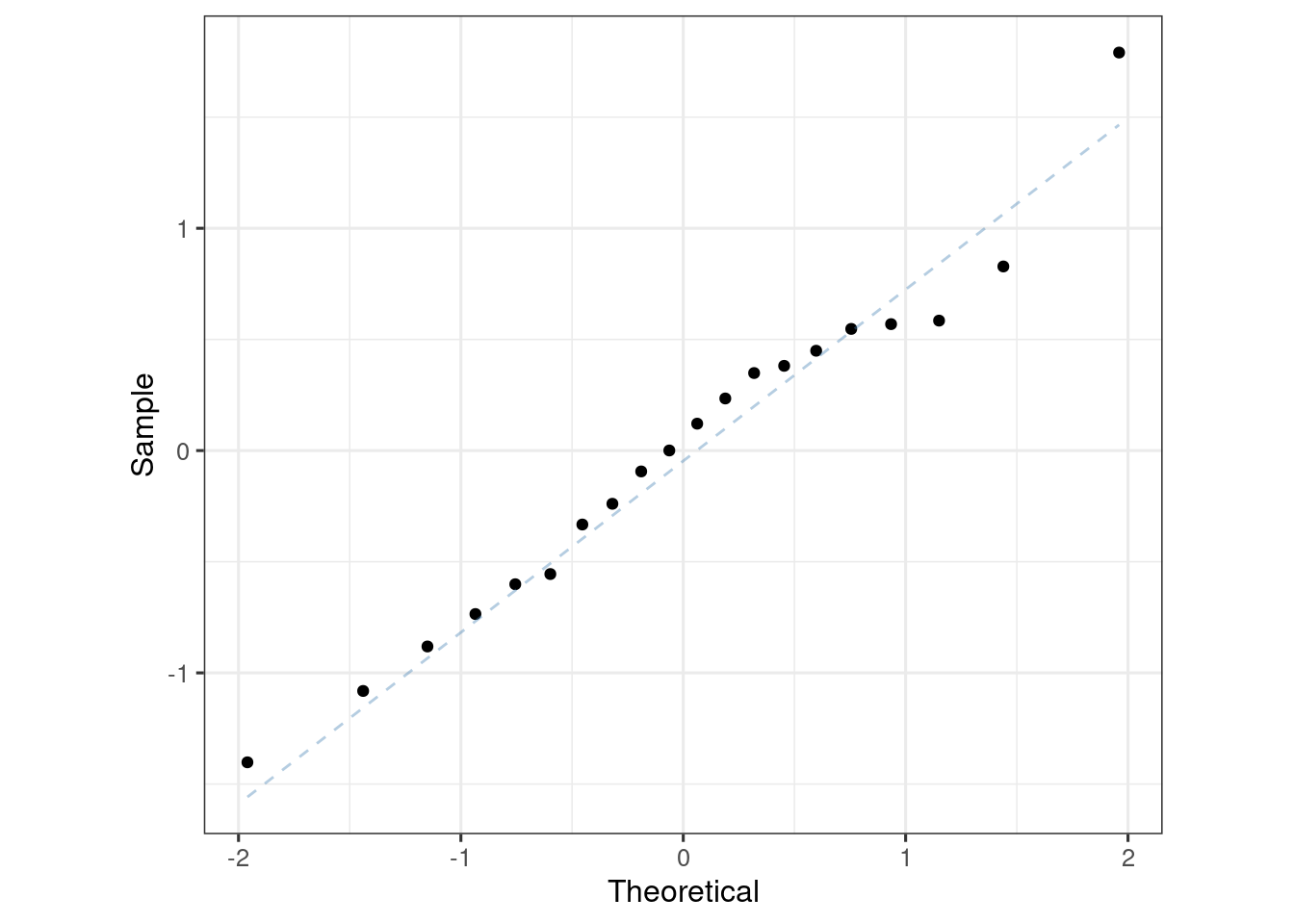
You can perform model comparison based on expected log pointwise predictive density (ELPD). ELPD is the Bayesian leave-one-out estimate (see ?loo-glossary).
Higher ELPD is better, therefore Emax model with γ fixed to be 1 appears better. However, elpd_diff is tiny and smaller than se_diff (see here), therefore we can consider the difference to be not meaningful.
loo_sigemax <- loo(ermod_sigemax)
loo_emax <- loo(ermod_emax)
loo_compare(list(sigemax = loo_sigemax, emax = loo_emax)) elpd_diff se_diff
emax 0.0 0.0
sigemax -0.9 0.4